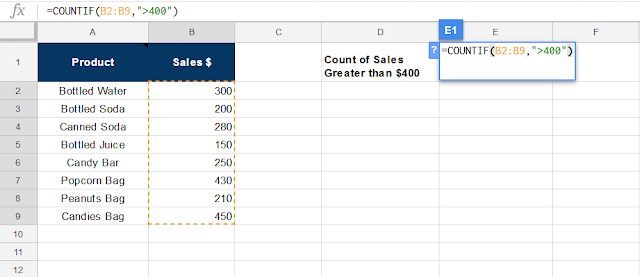
COUNTIF
Syntax
COUNTIF(range, criterion)
range- The range that is tested againstcriterion.criterion- The pattern or test to apply torange.If
rangecontains text to check against,criterionmust be a string.criterioncan contain wildcards including?to match any single character or*to match zero or more contiguous characters. To match an actual question mark or asterisk, prefix the character with the tilde (~) character (i.e.~?and~*). A string criterion must be enclosed in quotation marks. Each cell inrangeis then checked againstcriterionfor equality (or match, if wildcards are used).If
rangecontains numbers to check against,criterionmay be either a string or a number. If a number is provided, each cell inrangeis checked for equality withcriterion. Otherwise,criterionmay be a string containing a number (which also checks for equality), or a number prefixed with any of the following operators:=,>,>=,<, or<=, which check whether the range cell is equal to, greater than, greater than or equal to, less than, or less than or equal to the criterion value, respectively.
Notes
COUNTIFcan only perform conditional counts with a single criterion. To use multiple criteria, useCOUNTIFSor the database functionsDCOUNTorDCOUNTA.COUNTIFis not case sensitive.
Examples
See Also
COUNTIFS: Returns the count of a range depending on multiple criteria.
SUMIF: Returns a conditional sum across a range.
DCOUNTA: Counts values, including text, selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query.
DCOUNT: Counts numeric values selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query.
COUNTUNIQUE: Counts the number of unique values in a list of specified values and ranges.
COUNTA: Returns the number of values in a dataset.
COUNTBLANK: Returns the number of empty cells in a given range.
COUNT: Returns the number of numeric values in a dataset.